Predicting Columns in a Table - In Depth¶
Tip: If you are new to AutoGluon, review Predicting Columns in a Table - Quick Start to learn the basics of the AutoGluon API.
This tutorial describes how you can exert greater control when using
AutoGluon’s fit() by specifying the appropriate arguments. Using the
same census data table as Predicting Columns in a Table - Quick Start, we will try to
predict the occupation of an individual - a multi-class
classification problem.
Start by importing AutoGluon, specifying TabularPrediction as the task, and loading the data.
import autogluon as ag
from autogluon import TabularPrediction as task
train_data = task.Dataset(file_path='https://autogluon.s3.amazonaws.com/datasets/Inc/train.csv')
train_data = train_data.head(500) # subsample 500 data points for faster demo (comment this out to run on full dataset instead)
print(train_data.head())
val_data = task.Dataset(file_path='https://autogluon.s3.amazonaws.com/datasets/Inc/test.csv')
label_column = 'occupation'
print("Summary of occupation column: \n", train_data['occupation'].describe())
Loaded data from: https://autogluon.s3.amazonaws.com/datasets/Inc/train.csv | Columns = 15 / 15 | Rows = 39073 -> 39073
age workclass fnlwgt education education-num marital-status 0 25 Private 178478 Bachelors 13 Never-married
1 23 State-gov 61743 5th-6th 3 Never-married
2 46 Private 376789 HS-grad 9 Never-married
3 55 ? 200235 HS-grad 9 Married-civ-spouse
4 36 Private 224541 7th-8th 4 Married-civ-spouse
occupation relationship race sex capital-gain 0 Tech-support Own-child White Female 0
1 Transport-moving Not-in-family White Male 0
2 Other-service Not-in-family White Male 0
3 ? Husband White Male 0
4 Handlers-cleaners Husband White Male 0
capital-loss hours-per-week native-country class
0 0 40 United-States <=50K
1 0 35 United-States <=50K
2 0 15 United-States <=50K
3 0 50 United-States >50K
4 0 40 El-Salvador <=50K
Loaded data from: https://autogluon.s3.amazonaws.com/datasets/Inc/test.csv | Columns = 15 / 15 | Rows = 9769 -> 9769
Summary of occupation column:
count 500
unique 14
top Exec-managerial
freq 69
Name: occupation, dtype: object
To demonstrate how you can provide your own validation dataset against which AutoGluon tunes hyperparameters, we’ll use the test dataset from the previous tutorial as validation data.
If you don’t have a strong reason to provide your own validation
dataset, we recommend you omit the tuning_data argument. This lets
AutoGluon automatically select validation data from your provided
training set (it uses smart strategies such as stratified sampling). For
greater control, you can specify the holdout_frac argument to tell
AutoGluon what fraction of the provided training data to hold out for
validation.
Caution: Since AutoGluon tunes internal knobs based on this
validation data, performance estimates reported on this data may be
over-optimistic. For unbiased performance estimates, you should always
call predict() on a separate dataset (that was never passed to
fit()), as we did in the previous Quick-Start tutorial. We also
emphasize that most options specified in this tutorial are chosen to
minimize runtime for the purposes of demonstration and you should select
more reasonable values in order to obtain high-quality models.
fit() trains neural networks and various types of tree ensembles by
default. You can specify various hyperparameter values for each type of
model. For each hyperparameter, you can either specify a single fixed
value, or a search space of values to consider during the hyperparameter
optimization. Hyperparameters which you do not specify are left at
default settings chosen automatically by AutoGluon, which may be fixed
values or search spaces.
hp_tune = True # whether or not to do hyperparameter optimization
nn_options = { # specifies non-default hyperparameter values for neural network models
'num_epochs': 10, # number of training epochs (controls training time of NN models)
'learning_rate': ag.space.Real(1e-4, 1e-2, default=5e-4, log=True), # learning rate used in training (real-valued hyperparameter searched on log-scale)
'activation': ag.space.Categorical('relu', 'softrelu', 'tanh'), # activation function used in NN (categorical hyperparameter, default = first entry)
'layers': ag.space.Categorical([100],[1000],[200,100],[300,200,100]),
# Each choice for categorical hyperparameter 'layers' corresponds to list of sizes for each NN layer to use
'dropout_prob': ag.space.Real(0.0, 0.5, default=0.1), # dropout probability (real-valued hyperparameter)
}
gbm_options = { # specifies non-default hyperparameter values for lightGBM gradient boosted trees
'num_boost_round': 100, # number of boosting rounds (controls training time of GBM models)
'num_leaves': ag.space.Int(lower=26, upper=66, default=36), # number of leaves in trees (integer hyperparameter)
}
hyperparameters = {'NN': nn_options, 'GBM': gbm_options} # hyperparameters of each model type
# If one of these keys is missing from hyperparameters dict, then no models of that type are trained.
time_limits = 2*60 # train various models for ~2 min
num_trials = 5 # try at most 3 different hyperparameter configurations for each type of model
search_strategy = 'skopt' # to tune hyperparameters using SKopt Bayesian optimization routine
output_directory = 'agModels-predictOccupation' # folder where to store trained models
predictor = task.fit(train_data=train_data, tuning_data=val_data, label=label_column,
output_directory=output_directory, time_limits=time_limits, num_trials=num_trials,
hyperparameter_tune=hp_tune, hyperparameters=hyperparameters,
search_strategy=search_strategy)
/var/lib/jenkins/miniconda3/envs/autogluon_docs/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel/ipkernel.py:287: DeprecationWarning: should_run_async will not call transform_cell automatically in the future. Please pass the result to transformed_cell argument and any exception that happen during thetransform in preprocessing_exc_tuple in IPython 7.17 and above.
and should_run_async(code)
Warning: hyperparameter_tune=True is currently experimental and may cause the process to hang. Setting auto_stack=True instead is recommended to achieve maximum quality models.
Beginning AutoGluon training ... Time limit = 120s
AutoGluon will save models to agModels-predictOccupation/
AutoGluon Version: 0.0.13b20200814
Train Data Rows: 500
Train Data Columns: 15
Tuning Data Rows: 9769
Tuning Data Columns: 15
Preprocessing data ...
Here are the first 10 unique label values in your data: [' Tech-support', ' Transport-moving', ' Other-service', ' ?', ' Handlers-cleaners', ' Sales', ' Craft-repair', ' Adm-clerical', ' Exec-managerial', ' Prof-specialty']
AutoGluon infers your prediction problem is: multiclass (because dtype of label-column == object).
If this is wrong, please specify problem_type argument in fit() instead (You may specify problem_type as one of: ['binary', 'multiclass', 'regression'])
Warning: Some classes in the training set have fewer than 10 examples. AutoGluon will only keep 13 out of 14 classes for training and will not try to predict the rare classes. To keep more classes, increase the number of datapoints from these rare classes in the training data or reduce label_count_threshold.
Fraction of data from classes with at least 10 examples that will be kept for training models: 0.998
Train Data Class Count: 13
Feature Generator processed 10223 data points with 14 features
Original Features (raw dtypes):
int64 features: 6
object features: 8
Original Features (inferred dtypes):
int features: 6
object features: 8
Generated Features (special dtypes):
Processed Features (raw dtypes):
int features: 6
category features: 8
Processed Features:
int features: 6
category features: 8
Data preprocessing and feature engineering runtime = 0.09s ...
AutoGluon will gauge predictive performance using evaluation metric: accuracy
To change this, specify the eval_metric argument of fit()
AutoGluon will early stop models using evaluation metric: accuracy
scheduler_options: Key 'training_history_callback_delta_secs': Imputing default value 60
scheduler_options: Key 'delay_get_config': Imputing default value True
Starting Experiments
Num of Finished Tasks is 0
Num of Pending Tasks is 5
HBox(children=(FloatProgress(value=0.0, max=5.0), HTML(value='')))
Time out (secs) is 54.0
Ran out of time, early stopping on iteration 60. Best iteration is:
[60] train_set's multi_logloss: 1.90903 train_set's multi_error: 0.492986 valid_set's multi_logloss: 2.24104 valid_set's multi_error: 0.726964
0.2866 = Validation accuracy score
6.63s = Training runtime
0.05s = Validation runtime
0.2669 = Validation accuracy score
9.82s = Training runtime
0.12s = Validation runtime
0.2678 = Validation accuracy score
15.82s = Training runtime
0.26s = Validation runtime
0.2683 = Validation accuracy score
14.68s = Training runtime
0.05s = Validation runtime
0.273 = Validation accuracy score
5.83s = Training runtime
0.16s = Validation runtime
scheduler_options: Key 'training_history_callback_delta_secs': Imputing default value 60
scheduler_options: Key 'delay_get_config': Imputing default value True
Starting Experiments
Num of Finished Tasks is 0
Num of Pending Tasks is 5
HBox(children=(FloatProgress(value=0.0, max=5.0), HTML(value='')))
Time out (secs) is 54.0
Please either provide filename or allow plot in get_training_curves
0.1223 = Validation accuracy score
9.63s = Training runtime
0.85s = Validation runtime
0.177 = Validation accuracy score
9.59s = Training runtime
0.84s = Validation runtime
0.252 = Validation accuracy score
9.53s = Training runtime
0.85s = Validation runtime
0.2744 = Validation accuracy score
9.82s = Training runtime
0.86s = Validation runtime
0.2099 = Validation accuracy score
9.67s = Training runtime
0.86s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: weighted_ensemble_k0_l1 ... Training model for up to 119.91s of the 4.92s of remaining time.
0.2998 = Validation accuracy score
2.54s = Training runtime
0.0s = Validation runtime
AutoGluon training complete, total runtime = 117.65s ...
We again demonstrate how to use the trained models to predict on the validation data (We caution again that performance estimates here are biased because the same data was used to tune hyperparameters).
test_data = val_data.copy()
y_test = test_data[label_column]
test_data = test_data.drop(labels=[label_column],axis=1) # delete label column
y_pred = predictor.predict(test_data)
print("Predictions: ", list(y_pred)[:5])
perf = predictor.evaluate_predictions(y_true=y_test, y_pred=y_pred, auxiliary_metrics=False)
/var/lib/jenkins/miniconda3/envs/autogluon_docs/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel/ipkernel.py:287: DeprecationWarning: should_run_async will not call transform_cell automatically in the future. Please pass the result to transformed_cell argument and any exception that happen during thetransform in preprocessing_exc_tuple in IPython 7.17 and above. and should_run_async(code) Evaluation: accuracy on test data: 0.29839287542225407
Predictions: [' Other-service', ' ?', ' Exec-managerial', ' Sales', ' Other-service']
Use the following to view a summary of what happened during fit. This command will shows details of the hyperparameter-tuning process for each type of model:
results = predictor.fit_summary()
/var/lib/jenkins/miniconda3/envs/autogluon_docs/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel/ipkernel.py:287: DeprecationWarning: should_run_async will not call transform_cell automatically in the future. Please pass the result to transformed_cell argument and any exception that happen during thetransform in preprocessing_exc_tuple in IPython 7.17 and above. and should_run_async(code)
* Summary of fit() *
Estimated performance of each model:
model score_val pred_time_val fit_time pred_time_val_marginal fit_time_marginal stack_level can_infer
0 weighted_ensemble_k0_l1 0.299774 2.655593 52.832803 0.002180 2.539069 1 True
1 LightGBMClassifier/trial_0 0.286610 0.045378 6.634263 0.045378 6.634263 0 True
2 NeuralNetClassifier/trial_8 0.274373 0.861475 9.817652 0.861475 9.817652 0 True
3 LightGBMClassifier/trial_4 0.273036 0.163384 5.828573 0.163384 5.828573 0 True
4 LightGBMClassifier/trial_3 0.268305 0.048277 14.682018 0.048277 14.682018 0 True
5 LightGBMClassifier/trial_2 0.267791 0.264756 15.819246 0.264756 15.819246 0 True
6 LightGBMClassifier/trial_1 0.266865 0.119802 9.824280 0.119802 9.824280 0 True
7 NeuralNetClassifier/trial_7 0.251954 0.851146 9.531253 0.851146 9.531253 0 True
8 NeuralNetClassifier/trial_9 0.209893 0.855055 9.671326 0.855055 9.671326 0 True
9 NeuralNetClassifier/trial_6 0.176985 0.840080 9.586255 0.840080 9.586255 0 True
10 NeuralNetClassifier/trial_5 0.122275 0.847137 9.628548 0.847137 9.628548 0 True
Number of models trained: 11
Types of models trained:
{'WeightedEnsembleModel', 'TabularNeuralNetModel', 'LGBModel'}
Bagging used: False
Stack-ensembling used: False
Hyperparameter-tuning used: True
User-specified hyperparameters:
{'default': {'NN': [{'num_epochs': 10, 'learning_rate': Real: lower=0.0001, upper=0.01, 'activation': Categorical['relu', 'softrelu', 'tanh'], 'layers': Categorical[[100], [1000], [200, 100], [300, 200, 100]], 'dropout_prob': Real: lower=0.0, upper=0.5}], 'GBM': [{'num_boost_round': 100, 'num_leaves': Int: lower=26, upper=66}]}}
Plot summary of models saved to file: agModels-predictOccupation/SummaryOfModels.html
Plot summary of models saved to file: agModels-predictOccupation/LightGBMClassifier_HPOmodelsummary.html
Plot summary of models saved to file: LightGBMClassifier_HPOmodelsummary.html
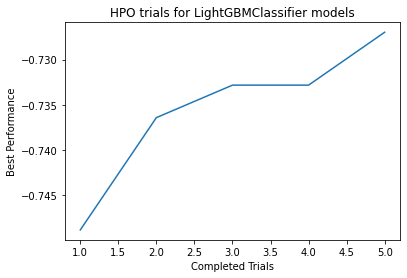
Plot of HPO performance saved to file: agModels-predictOccupation/LightGBMClassifier_HPOperformanceVStrials.png
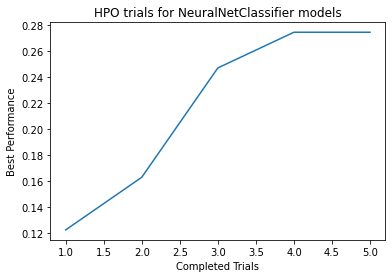
Plot summary of models saved to file: agModels-predictOccupation/NeuralNetClassifier_HPOmodelsummary.html
Plot summary of models saved to file: NeuralNetClassifier_HPOmodelsummary.html
Plot of HPO performance saved to file: agModels-predictOccupation/NeuralNetClassifier_HPOperformanceVStrials.png
* Details of Hyperparameter optimization *
HPO for LightGBMClassifier model: Num. configurations tried = 5, Time spent = 54.389808654785156, Search strategy = skopt
Best hyperparameter-configuration (validation-performance: accuracy = -0.7269642122583299):
{'feature_fraction': 0.8929120631955865, 'learning_rate': 0.008967035891539783, 'min_data_in_leaf': 13, 'num_leaves': 60}
HPO for NeuralNetClassifier model: Num. configurations tried = 5, Time spent = 53.84730577468872, Search strategy = skopt
Best hyperparameter-configuration (validation-performance: accuracy = 0.274372686137392):
{'activation▁choice': 0, 'dropout_prob': 0.28516573180036303, 'embedding_size_factor': 0.7957435177080714, 'layers▁choice': 1, 'learning_rate': 0.003860737803953105, 'network_type▁choice': 0, 'use_batchnorm▁choice': 1, 'weight_decay': 8.36647279794633e-06}
* End of fit() summary *
In the above example, the predictive performance may be poor because we
specified very little training to ensure quick runtimes. You can call
fit() multiple times while modifying the above settings to better
understand how these choices affect performance outcomes. For example:
you can comment out the train_data.head command to train using a
larger dataset, increase the time_limits, and increase the
num_epochs and num_boost_round hyperparameters. To see more
detailed output during the execution of fit(), you can also pass in
the argument: verbosity = 3.
Specifying performance metrics¶
Performance in certain applications may be measured by different metrics than the ones AutoGluon optimizes for by default. If you know the metric that counts most in your application, you can specify it as done below to utilize the balanced accuracy metric instead of standard accuracy (the default):
metric = 'balanced_accuracy'
predictor = task.fit(train_data=train_data, label=label_column, eval_metric=metric,
output_directory=output_directory, time_limits=60)
performance = predictor.evaluate(val_data)
/var/lib/jenkins/miniconda3/envs/autogluon_docs/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel/ipkernel.py:287: DeprecationWarning: should_run_async will not call transform_cell automatically in the future. Please pass the result to transformed_cell argument and any exception that happen during thetransform in preprocessing_exc_tuple in IPython 7.17 and above.
and should_run_async(code)
Beginning AutoGluon training ... Time limit = 60s
AutoGluon will save models to agModels-predictOccupation/
AutoGluon Version: 0.0.13b20200814
Train Data Rows: 500
Train Data Columns: 15
Preprocessing data ...
Here are the first 10 unique label values in your data: [' Tech-support', ' Transport-moving', ' Other-service', ' ?', ' Handlers-cleaners', ' Sales', ' Craft-repair', ' Adm-clerical', ' Exec-managerial', ' Prof-specialty']
AutoGluon infers your prediction problem is: multiclass (because dtype of label-column == object).
If this is wrong, please specify problem_type argument in fit() instead (You may specify problem_type as one of: ['binary', 'multiclass', 'regression'])
Warning: Some classes in the training set have fewer than 10 examples. AutoGluon will only keep 13 out of 14 classes for training and will not try to predict the rare classes. To keep more classes, increase the number of datapoints from these rare classes in the training data or reduce label_count_threshold.
Fraction of data from classes with at least 10 examples that will be kept for training models: 0.998
Train Data Class Count: 13
Feature Generator processed 499 data points with 14 features
Original Features (raw dtypes):
int64 features: 6
object features: 8
Original Features (inferred dtypes):
int features: 6
object features: 8
Generated Features (special dtypes):
Processed Features (raw dtypes):
int features: 6
category features: 8
Processed Features:
int features: 6
category features: 8
Data preprocessing and feature engineering runtime = 0.05s ...
AutoGluon will gauge predictive performance using evaluation metric: balanced_accuracy
To change this, specify the eval_metric argument of fit()
AutoGluon will early stop models using evaluation metric: balanced_accuracy
Fitting model: RandomForestClassifierGini ... Training model for up to 59.95s of the 59.95s of remaining time.
0.2232 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
0.61s = Training runtime
0.11s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: RandomForestClassifierEntr ... Training model for up to 59.2s of the 59.2s of remaining time.
0.2499 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
0.6s = Training runtime
0.11s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: ExtraTreesClassifierGini ... Training model for up to 58.46s of the 58.46s of remaining time.
0.2139 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
0.5s = Training runtime
0.11s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: ExtraTreesClassifierEntr ... Training model for up to 57.81s of the 57.81s of remaining time.
0.2018 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
0.5s = Training runtime
0.11s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: KNeighborsClassifierUnif ... Training model for up to 57.16s of the 57.16s of remaining time.
0.0902 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
0.0s = Training runtime
0.1s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: KNeighborsClassifierDist ... Training model for up to 57.05s of the 57.05s of remaining time.
0.1136 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
0.0s = Training runtime
0.1s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: LightGBMClassifier ... Training model for up to 56.94s of the 56.94s of remaining time.
0.2171 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
7.06s = Training runtime
0.01s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: CatboostClassifier ... Training model for up to 49.86s of the 49.86s of remaining time.
0.2852 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
5.53s = Training runtime
0.01s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: NeuralNetClassifier ... Training model for up to 44.31s of the 44.31s of remaining time.
0.1565 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
3.51s = Training runtime
0.03s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: LightGBMClassifierCustom ... Training model for up to 40.77s of the 40.77s of remaining time.
Ran out of time, early stopping on iteration 145. Best iteration is:
[133] train_set's multi_logloss: 0.0993952 train_set's balanced_accuracy: 1 valid_set's multi_logloss: 2.73162 valid_set's balanced_accuracy: 0.195132
0.1951 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
41.34s = Training runtime
0.02s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: weighted_ensemble_k0_l1 ... Training model for up to 59.95s of the -1.95s of remaining time.
0.301 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
0.53s = Training runtime
0.0s = Validation runtime
AutoGluon training complete, total runtime = 62.5s ...
Predictive performance on given dataset: balanced_accuracy = 0.24734433302235082
Some other non-default metrics you might use include things like: f1
(for binary classification), roc_auc (for binary classification),
log_loss (for classification), mean_absolute_error (for
regression), median_absolute_error (for regression). You can also
define your own custom metric function, see examples in the folder:
autogluon/utils/tabular/metrics/
Model ensembling with stacking/bagging¶
Beyond hyperparameter-tuning with a correctly-specified evaluation
metric, two other methods to boost predictive performance are bagging
and stack-ensembling. You’ll often see performance improve if you
specify num_bagging_folds = 5-10, stack_ensemble_levels = 1-3 in
the call to fit(), but this will increase training times.
predictor = task.fit(train_data=train_data, label=label_column, eval_metric=metric,
num_bagging_folds=5, stack_ensemble_levels=1,
hyperparameters = {'NN':{'num_epochs':5}, 'GBM':{'num_boost_round':100}})
/var/lib/jenkins/miniconda3/envs/autogluon_docs/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel/ipkernel.py:287: DeprecationWarning: should_run_async will not call transform_cell automatically in the future. Please pass the result to transformed_cell argument and any exception that happen during thetransform in preprocessing_exc_tuple in IPython 7.17 and above.
and should_run_async(code)
No output_directory specified. Models will be saved in: AutogluonModels/ag-20200814_201726/
Beginning AutoGluon training ...
AutoGluon will save models to AutogluonModels/ag-20200814_201726/
AutoGluon Version: 0.0.13b20200814
Train Data Rows: 500
Train Data Columns: 15
Preprocessing data ...
Here are the first 10 unique label values in your data: [' Tech-support', ' Transport-moving', ' Other-service', ' ?', ' Handlers-cleaners', ' Sales', ' Craft-repair', ' Adm-clerical', ' Exec-managerial', ' Prof-specialty']
AutoGluon infers your prediction problem is: multiclass (because dtype of label-column == object).
If this is wrong, please specify problem_type argument in fit() instead (You may specify problem_type as one of: ['binary', 'multiclass', 'regression'])
Warning: Some classes in the training set have fewer than 10 examples. AutoGluon will only keep 13 out of 14 classes for training and will not try to predict the rare classes. To keep more classes, increase the number of datapoints from these rare classes in the training data or reduce label_count_threshold.
Fraction of data from classes with at least 10 examples that will be kept for training models: 0.998
Train Data Class Count: 13
Feature Generator processed 499 data points with 14 features
Original Features (raw dtypes):
int64 features: 6
object features: 8
Original Features (inferred dtypes):
int features: 6
object features: 8
Generated Features (special dtypes):
Processed Features (raw dtypes):
int features: 6
category features: 8
Processed Features:
int features: 6
category features: 8
Data preprocessing and feature engineering runtime = 0.06s ...
AutoGluon will gauge predictive performance using evaluation metric: balanced_accuracy
To change this, specify the eval_metric argument of fit()
AutoGluon will early stop models using evaluation metric: balanced_accuracy
Fitting model: LightGBMClassifier_STACKER_l0 ...
0.2122 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
21.9s = Training runtime
0.05s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: NeuralNetClassifier_STACKER_l0 ...
0.0996 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
2.99s = Training runtime
0.15s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: weighted_ensemble_k0_l1 ...
0.2122 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
0.19s = Training runtime
0.0s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: LightGBMClassifier_STACKER_l1 ...
0.2154 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
23.22s = Training runtime
0.07s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: NeuralNetClassifier_STACKER_l1 ...
0.1014 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
3.11s = Training runtime
0.18s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: weighted_ensemble_k0_l2 ...
0.2154 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
0.19s = Training runtime
0.0s = Validation runtime
AutoGluon training complete, total runtime = 52.41s ...
You should not provide tuning_data when stacking/bagging, and
instead provide all your available data as train_data (which
AutoGluon will split in more intellgent ways). Rather than manually
searching for good bagging/stacking values yourself, AutoGluon will
automatically select good values for you if you specify auto_stack
instead:
predictor = task.fit(train_data=train_data, label=label_column, eval_metric=metric, auto_stack=True,
hyperparameters = {'NN':{'num_epochs':5}, 'GBM':{'num_boost_round':100}}, time_limits = 60) # last 2 arguments are just for quick demo, should be omitted
/var/lib/jenkins/miniconda3/envs/autogluon_docs/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel/ipkernel.py:287: DeprecationWarning: should_run_async will not call transform_cell automatically in the future. Please pass the result to transformed_cell argument and any exception that happen during thetransform in preprocessing_exc_tuple in IPython 7.17 and above.
and should_run_async(code)
No output_directory specified. Models will be saved in: AutogluonModels/ag-20200814_201818/
Beginning AutoGluon training ... Time limit = 60s
AutoGluon will save models to AutogluonModels/ag-20200814_201818/
AutoGluon Version: 0.0.13b20200814
Train Data Rows: 500
Train Data Columns: 15
Preprocessing data ...
Here are the first 10 unique label values in your data: [' Tech-support', ' Transport-moving', ' Other-service', ' ?', ' Handlers-cleaners', ' Sales', ' Craft-repair', ' Adm-clerical', ' Exec-managerial', ' Prof-specialty']
AutoGluon infers your prediction problem is: multiclass (because dtype of label-column == object).
If this is wrong, please specify problem_type argument in fit() instead (You may specify problem_type as one of: ['binary', 'multiclass', 'regression'])
Warning: Some classes in the training set have fewer than 10 examples. AutoGluon will only keep 13 out of 14 classes for training and will not try to predict the rare classes. To keep more classes, increase the number of datapoints from these rare classes in the training data or reduce label_count_threshold.
Fraction of data from classes with at least 10 examples that will be kept for training models: 0.998
Train Data Class Count: 13
Feature Generator processed 499 data points with 14 features
Original Features (raw dtypes):
int64 features: 6
object features: 8
Original Features (inferred dtypes):
int features: 6
object features: 8
Generated Features (special dtypes):
Processed Features (raw dtypes):
int features: 6
category features: 8
Processed Features:
int features: 6
category features: 8
Data preprocessing and feature engineering runtime = 0.05s ...
AutoGluon will gauge predictive performance using evaluation metric: balanced_accuracy
To change this, specify the eval_metric argument of fit()
AutoGluon will early stop models using evaluation metric: balanced_accuracy
Fitting model: LightGBMClassifier_STACKER_l0 ... Training model for up to 59.95s of the 59.95s of remaining time.
0.2122 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
21.91s = Training runtime
0.05s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: NeuralNetClassifier_STACKER_l0 ... Training model for up to 37.91s of the 37.91s of remaining time.
0.0825 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
3.0s = Training runtime
0.16s = Validation runtime
Repeating k-fold bagging: 2/20
Fitting model: LightGBMClassifier_STACKER_l0 ... Training model for up to 34.71s of the 34.71s of remaining time.
0.2021 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
43.8s = Training runtime
0.11s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: NeuralNetClassifier_STACKER_l0 ... Training model for up to 12.72s of the 12.72s of remaining time.
0.0816 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
6.01s = Training runtime
0.31s = Validation runtime
Completed 2/20 k-fold bagging repeats ...
Fitting model: weighted_ensemble_k0_l1 ... Training model for up to 59.95s of the 9.53s of remaining time.
0.2055 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
0.19s = Training runtime
0.0s = Validation runtime
AutoGluon training complete, total runtime = 50.67s ...
Getting predictions (inference-time options)¶
Even if you’ve started a new Python session since last calling
fit(), you can still load a previously trained predictor from disk:
predictor = task.load(output_directory)
/var/lib/jenkins/miniconda3/envs/autogluon_docs/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel/ipkernel.py:287: DeprecationWarning: should_run_async will not call transform_cell automatically in the future. Please pass the result to transformed_cell argument and any exception that happen during thetransform in preprocessing_exc_tuple in IPython 7.17 and above. and should_run_async(code)
Here, output_directory is the same folder previously passed to
fit(), in which all the trained models have been saved. You can
train easily models on one machine and deploy them on another. Simply
copy the output_directory folder to the new machine and specify its
new path in task.load().
predictor can make a prediction on an individual example rather than
a full dataset:
datapoint = test_data.iloc[[0]] # Note: .iloc[0] won't work because it returns pandas Series instead of DataFrame
print(datapoint)
print(predictor.predict(datapoint))
age workclass fnlwgt education education-num marital-status 0 31 Private 169085 11th 7 Married-civ-spouse relationship race sex capital-gain capital-loss hours-per-week 0 Wife White Female 0 0 20 native-country class 0 United-States <=50K [' Other-service']
To output predicted class probabilities instead of predicted classes, you can use:
class_probs = predictor.predict_proba(datapoint)
print(class_probs)
/var/lib/jenkins/miniconda3/envs/autogluon_docs/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel/ipkernel.py:287: DeprecationWarning: should_run_async will not call transform_cell automatically in the future. Please pass the result to transformed_cell argument and any exception that happen during thetransform in preprocessing_exc_tuple in IPython 7.17 and above. and should_run_async(code)
[[0.02349734 0.15290621 0.06299862 0.08908273 0.0224535 0.04816712
0.09885164 0.23454452 0. 0.07250251 0.021852 0.09218392
0.03025525 0.05070464]]
By default, predict() and predict_proba() will utilize the model
that AutoGluon thinks is most accurate, which is usually an ensemble of
many individual models. We can instead specify a particular model to use
for predictions (e.g. to reduce inference latency). Before deciding
which model to use, let’s evaluate all of the models AutoGluon has
previously trained using our validation dataset:
results = predictor.leaderboard(val_data)
/var/lib/jenkins/miniconda3/envs/autogluon_docs/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel/ipkernel.py:287: DeprecationWarning: should_run_async will not call transform_cell automatically in the future. Please pass the result to transformed_cell argument and any exception that happen during thetransform in preprocessing_exc_tuple in IPython 7.17 and above. and should_run_async(code)
model score_test score_val pred_time_test pred_time_val fit_time pred_time_test_marginal pred_time_val_marginal fit_time_marginal stack_level can_infer
0 weighted_ensemble_k0_l1 0.247344 0.300951 2.782021 0.607805 59.692959 0.012318 0.001010 0.534558 1 True
1 CatboostClassifier 0.242090 0.285176 0.046196 0.012144 5.532541 0.046196 0.012144 5.532541 0 True
2 RandomForestClassifierGini 0.237777 0.223151 0.229422 0.110487 0.607831 0.229422 0.110487 0.607831 0 True
3 RandomForestClassifierEntr 0.236948 0.249942 0.228999 0.110721 0.604720 0.228999 0.110721 0.604720 0 True
4 ExtraTreesClassifierEntr 0.231815 0.201839 0.248649 0.110626 0.500701 0.248649 0.110626 0.500701 0 True
5 ExtraTreesClassifierGini 0.230390 0.213904 0.255234 0.110618 0.501093 0.255234 0.110618 0.501093 0 True
6 LightGBMClassifier 0.196499 0.217144 0.033086 0.010741 7.063791 0.033086 0.010741 7.063791 0 True
7 LightGBMClassifierCustom 0.178989 0.195132 0.518744 0.016568 41.335205 0.518744 0.016568 41.335205 0 True
8 NeuralNetClassifier 0.159724 0.156478 1.247532 0.029639 3.508746 1.247532 0.029639 3.508746 0 True
9 KNeighborsClassifierUnif 0.073979 0.090152 0.104676 0.102971 0.002285 0.104676 0.102971 0.002285 0 True
10 KNeighborsClassifierDist 0.071566 0.113624 0.105814 0.102908 0.002189 0.105814 0.102908 0.002189 0 True
Here’s how to specify a particular model to use for prediction instead of AutoGluon’s default model-choice:
i = 0 # index of model to use
model_to_use = predictor.model_names[i]
model_pred = predictor.predict(datapoint, model=model_to_use)
print("Prediction from %s model: %s" % (model_to_use, model_pred))
/var/lib/jenkins/miniconda3/envs/autogluon_docs/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel/ipkernel.py:287: DeprecationWarning: should_run_async will not call transform_cell automatically in the future. Please pass the result to transformed_cell argument and any exception that happen during thetransform in preprocessing_exc_tuple in IPython 7.17 and above. and should_run_async(code) WARNING: predictor.model_names is a deprecated predictor variable. Use predictor.get_model_names() instead. Use of predictor.model_names will result in an exception starting in autogluon==0.1
Prediction from RandomForestClassifierGini model: [' Other-service']
The predictor also remembers what metric predictions should be
evaluated with, which can be done with ground truth labels as follows:
y_pred = predictor.predict(test_data)
predictor.evaluate_predictions(y_true=y_test, y_pred=y_pred, auxiliary_metrics=True)
However, you must be careful here as certain metrics require predicted
probabilities rather than classes. Since the label columns remains in
the val_data DataFrame, we can instead use the shorthand:
predictor.evaluate(val_data)
which will correctly select between predict() or predict_proba()
depending on the evaluation metric.
Maximizing predictive performance¶
To get the best predictive accuracy with AutoGluon, you should generally use it like this:
long_time = 60 # for quick demonstration only, you should set this to longest time you are willing to wait
predictor = task.fit(train_data=train_data, label=label_column, eval_metric=metric, auto_stack=True, time_limits=long_time)
/var/lib/jenkins/miniconda3/envs/autogluon_docs/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel/ipkernel.py:287: DeprecationWarning: should_run_async will not call transform_cell automatically in the future. Please pass the result to transformed_cell argument and any exception that happen during thetransform in preprocessing_exc_tuple in IPython 7.17 and above.
and should_run_async(code)
No output_directory specified. Models will be saved in: AutogluonModels/ag-20200814_201913/
Beginning AutoGluon training ... Time limit = 60s
AutoGluon will save models to AutogluonModels/ag-20200814_201913/
AutoGluon Version: 0.0.13b20200814
Train Data Rows: 500
Train Data Columns: 15
Preprocessing data ...
Here are the first 10 unique label values in your data: [' Tech-support', ' Transport-moving', ' Other-service', ' ?', ' Handlers-cleaners', ' Sales', ' Craft-repair', ' Adm-clerical', ' Exec-managerial', ' Prof-specialty']
AutoGluon infers your prediction problem is: multiclass (because dtype of label-column == object).
If this is wrong, please specify problem_type argument in fit() instead (You may specify problem_type as one of: ['binary', 'multiclass', 'regression'])
Warning: Some classes in the training set have fewer than 10 examples. AutoGluon will only keep 13 out of 14 classes for training and will not try to predict the rare classes. To keep more classes, increase the number of datapoints from these rare classes in the training data or reduce label_count_threshold.
Fraction of data from classes with at least 10 examples that will be kept for training models: 0.998
Train Data Class Count: 13
Feature Generator processed 499 data points with 14 features
Original Features (raw dtypes):
int64 features: 6
object features: 8
Original Features (inferred dtypes):
int features: 6
object features: 8
Generated Features (special dtypes):
Processed Features (raw dtypes):
int features: 6
category features: 8
Processed Features:
int features: 6
category features: 8
Data preprocessing and feature engineering runtime = 0.05s ...
AutoGluon will gauge predictive performance using evaluation metric: balanced_accuracy
To change this, specify the eval_metric argument of fit()
AutoGluon will early stop models using evaluation metric: balanced_accuracy
Fitting model: RandomForestClassifierGini_STACKER_l0 ... Training model for up to 59.95s of the 59.95s of remaining time.
0.2257 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
3.05s = Training runtime
0.55s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: RandomForestClassifierEntr_STACKER_l0 ... Training model for up to 56.21s of the 56.21s of remaining time.
0.2115 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
3.05s = Training runtime
0.55s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: ExtraTreesClassifierGini_STACKER_l0 ... Training model for up to 52.48s of the 52.48s of remaining time.
0.2214 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
2.53s = Training runtime
0.55s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: ExtraTreesClassifierEntr_STACKER_l0 ... Training model for up to 49.2s of the 49.2s of remaining time.
0.212 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
2.52s = Training runtime
0.55s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: KNeighborsClassifierUnif_STACKER_l0 ... Training model for up to 45.93s of the 45.93s of remaining time.
0.0689 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
0.02s = Training runtime
0.51s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: KNeighborsClassifierDist_STACKER_l0 ... Training model for up to 45.39s of the 45.39s of remaining time.
0.0708 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
0.02s = Training runtime
0.51s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: LightGBMClassifier_STACKER_l0 ... Training model for up to 44.84s of the 44.84s of remaining time.
Ran out of time, early stopping on iteration 166. Best iteration is:
[25] train_set's multi_logloss: 1.29038 train_set's balanced_accuracy: 0.625395 valid_set's multi_logloss: 2.27283 valid_set's balanced_accuracy: 0.220647
Ran out of time, early stopping on iteration 174. Best iteration is:
[82] train_set's multi_logloss: 0.478952 train_set's balanced_accuracy: 0.985162 valid_set's multi_logloss: 2.56851 valid_set's balanced_accuracy: 0.227756
Ran out of time, early stopping on iteration 185. Best iteration is:
[37] train_set's multi_logloss: 1.00849 train_set's balanced_accuracy: 0.789105 valid_set's multi_logloss: 2.37467 valid_set's balanced_accuracy: 0.175384
0.2122 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
37.81s = Training runtime
0.05s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: CatboostClassifier_STACKER_l0 ... Training model for up to 6.91s of the 6.91s of remaining time.
0.2677 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
6.53s = Training runtime
0.04s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: NeuralNetClassifier_STACKER_l0 ... Training model for up to 0.33s of the 0.33s of remaining time.
Ran out of time, stopping training early.
Time limit exceeded... Skipping NeuralNetClassifier_STACKER_l0.
Fitting model: LightGBMClassifierCustom_STACKER_l0 ... Training model for up to 0.01s of the 0.01s of remaining time.
Ran out of time, early stopping on iteration 1. Best iteration is:
[1] train_set's multi_logloss: 2.31795 train_set's balanced_accuracy: 0.104072 valid_set's multi_logloss: 2.4097 valid_set's balanced_accuracy: 0.0774162
Time limit exceeded... Skipping LightGBMClassifierCustom_STACKER_l0.
Completed 1/20 k-fold bagging repeats ...
Fitting model: weighted_ensemble_k0_l1 ... Training model for up to 59.95s of the -0.26s of remaining time.
0.2692 = Validation balanced_accuracy score
0.58s = Training runtime
0.0s = Validation runtime
AutoGluon training complete, total runtime = 60.86s ...
This command implements the following strategy to maximize accuracy:
Specify the
auto_stackargument, which allows AutoGluon to automatically construct model ensembles based on multi-layer stack ensembling with repeated bagging, and will greatly improve the resulting predictions if granted sufficient training time.Provide the
eval_metricif you know what metric will be used to evaluate predictions in your application (e.g.roc_auc,log_loss,mean_absolute_error, etc.)Include all your data in
train_dataand do not providetuning_data(AutoGluon will split the data more intelligently to fit its needs).Do not specify the
hyperparameter_tuneargument (counterintuitively, hyperparameter tuning is not the best way to spend a limited training time budgets, as model ensembling is often superior). We recommend you only usehyperparameter_tuneif your goal is to deploy a single model rather than an ensemble.Do not specify
hyperparametersargument (allow AutoGluon to adaptively select which models/hyperparameters to use).Set
time_limitsto the longest amount of time (in seconds) that you are willing to wait. AutoGluon’s predictive performance improves the longerfit()is allowed to run.